Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIg) Therapy
Frequently Asked Questions
This document has been developed by ASCIA, the peak professional body of clinical immunology/allergy specialists in Australia and New Zealand. ASCIA information is based on published literature and expert review, is not influenced by commercial organisations and is not intended to replace medical advice.
For patient or carer support contact AusPIPS, IDFA, or IDFNZ.
![]() ASCIA PC PID-IEI SCIg General Information FAQ 2025625.26 KB
ASCIA PC PID-IEI SCIg General Information FAQ 2025625.26 KB
Q 1: What is SCIg?
Immunoglobulins (commonly known as antibodies) are used to treat adults and children with some inborn errors of immunity (IEI), including primary immune deficiencies (PID), and other medical conditions, who are unable to make enough of their own antibodies, or who have antibodies that don’t work properly.
Replacing these antibodies helps to protect against infection and can prevent long term damage from ongoing infections, such as chronic lung disease.
Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIg) infusions are given by slowly injecting purified immunoglobulin into fatty tissue just underneath the skin. SCIg:
- Requires frequent administration (ranging from 1-3 times per week to once a fortnight) by patients or carers at home.
- Involves slow diffusion of IgG from subcutaneous tissue.
- Is associated with more consistent serum IgG levels due to frequent administration.
- Is administered at multiple injection sites according to personal preference, usually in the lower abdomen. However, the outer edge of the thigh or back of the upper arm can also be used.
Q 2: How are SCIg infusions given?
SCIg can be given at home using:
- Mechanical infusion pumps - spring loaded or battery powered.
- Push method - a manual method that does not require a pump, with the infusion pushed by hand through a syringe.
Q 3: Are immunoglobulin products safe?
SCIg is very well tolerated and safe. SCIg is made from plasma (the liquid part of blood), which comes from blood donors who are checked to make sure they are healthy and do not have certain infectious diseases.
Manufacturers also include steps in the processing of blood or plasma that inactivate or remove viruses.
This means that there is an extremely low (almost zero) chance of the transmission of blood borne viruses (such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HIV and Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (also called “mad cow disease”) via SCIg.
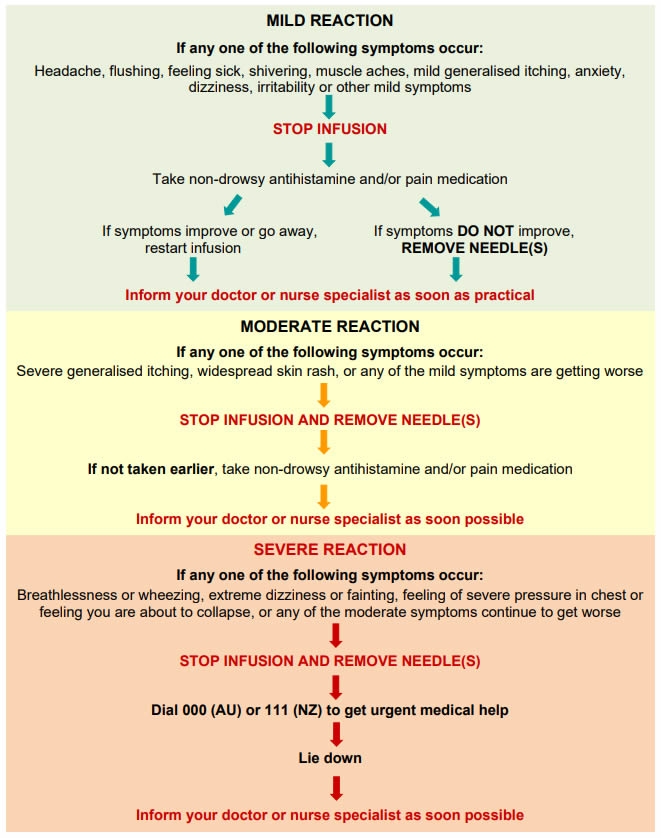
Q 4: What are the risks associated with SCIg?
Reactions or side effects to SCIg include:
- Common injection site reactions such as redness, swelling and itching.
- These are usually mild and go away over a day or two.
- Reactions are generally worse with the first few infusions and get better over time.
- Most itching is resolved by slowing the infusion.
- Uncommon side effects such as headache, feeling hot, nausea, diarrhoea, sore throat, rash, increased cough and back pain.
- These are usually mild.
- Extremely rare and serious side effects such as allergic reactions, kidney problems or blood clots.
If a reaction occurs you must inform your nurse specialist or doctor as soon as possible and get advice before having any more infusions.
For information about managing reactions here.
Q 5: What needs to be done before starting SCIg?
Before you start on SCIg, your nurse specialist will provide you with information and training on how to give SCIg at home. Nurses play a crucial role in educating and supporting people who are being treated with immunoglobulin products.
You will need to sign a consent form to say that you understand the need for treatment and the chance of reactions that may occur with the treatment.
 An ASCIA Treatment Summary for patients is available at www.allergy.org.au/hp/papers/ascia-transfer-care-plan-irt
An ASCIA Treatment Summary for patients is available at www.allergy.org.au/hp/papers/ascia-transfer-care-plan-irt
This plan has been developed as a medical document to be completed by an immunology or nurse specialist, when a patient is transferring/transitioning from:
- Paediatric to adult medical care.
- One region to another.
- IVIg to SCIg.
- SCIg to IVIg.
Q 6: How are SCIg infusion sites chosen?
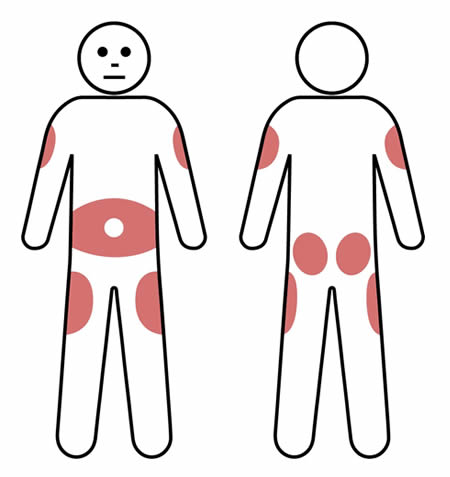 Using the same site for infusions can help reduce the amount of local swelling and redness that can occur after an infusion.
Using the same site for infusions can help reduce the amount of local swelling and redness that can occur after an infusion.
However, multiple (2-3) sites can be used on a rotating basis, according to patient preference.
Rotating the infusion site is preferable for some patients and this may reduce the risk of scar tissue developing.
SCIg injection sites are usually in the lower abdomen, but the outer edge of the thigh, buttocks or back of the upper arm can also be used. Avoid bony areas such as the hips.
When using the lower abdomen in adults and most children, the needle should be inserted at least 5cm away from the belly button.
If using more than one site at a time, make sure they are at least 5cm apart.
Note: Do not insert the needle where the skin is scarred, bruised, broken or inflamed (such as eczema).
Before infusion it is important to have your equipment ready – see the ASCIA Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIg) Equipment Checklist www.allergy.org.au/patients/immunodeficiencies/scig-therapy-equipment-checklist
The ASCIA Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIg) Infusion Checklist for the process of infusion is also useful. www.allergy.org.au/patients/immunodeficiencies/scig-infusion-checklist
It is recommended to have a cold pack, a non-drowsy antihistamine and an analgesic (pain medication) available in case of a mild reaction.
Examples of SCIg infusions are shown below.
Q 7: How should SCIg infusions be documented?
Patients should record the following details in a SCIg infusion diary, which can be shown to the nurse or medical specialist:
- Brand of SCIg product.
- Batch number/sticker.
- Date and time of infusion.
- Time taken for infusion.
- Dose
- Reactions to infusion.
- Problems with product (e.g. visible particles - not used and returned).
- Unused or wasted product (e.g. spilled/damaged or infusion stopped due to adverse reaction).
Q 8: How is SCIg ordered, collected, transported and stored?
 Use the ASCIA SCIg Treatment Plan, which is available on the ASCIA website allergy.org.au/hp/papers/ascia-scig-treatment-plan
Use the ASCIA SCIg Treatment Plan, which is available on the ASCIA website allergy.org.au/hp/papers/ascia-scig-treatment-plan- SCIg product needs to be ordered in advance.
- Your nurse specialist or doctor will explain how and where to collect the SCIg product, and this should be included in your SCIg treatment plan.
- SCIg must be kept cool (2-8°C) for the journey home:
- When collecting SCIg you must provide a cool box or cool bag large enough to transport vials with an icepack. Ensure SCIg vials are not in direct contact with the ice, to avoid possible freezing.
- Take SCIg home immediately and place in a sealed container in the central part of the refrigerator.
- Storage temperatures are dependent on product choice (refer to information about each product below). Your nurse or medical specialist will advise you how to store the specific SCIg product you are using. However, the following principles should be followed for all SCIg products:
![]() Store SCIg in original packaging until needed, and protected from light
Store SCIg in original packaging until needed, and protected from light![]() Store SCIg between 2°C and 25°C and avoid extreme temperatures.
Store SCIg between 2°C and 25°C and avoid extreme temperatures. ![]() Do not freeze SCIg - never store below 2oC and do not use SCIg that has been frozen.
Do not freeze SCIg - never store below 2oC and do not use SCIg that has been frozen. ![]() Do not shake SCIg.
Do not shake SCIg.
If you have a power or refrigerator failure and are unable to keep SCIg refrigerated:
- Contact your nurse specialist as soon as practical for further advice.
- If fridge is still cold, keep your supply in the fridge.
- If the fridge is no longer cold, place SCIg in your transport cool box or cool bag with an ice pack.
Product from a vial is for single use only
- Once the vial is opened, SCIg needs to be used as soon as possible as the product does not contain preservative.
- If an infusion cannot be completed within the recommended time (which varies between 2 and 4 hours for different products), any unused product should be discarded.
- All SCIg vials must be disposed of in the sharps container provided by your hospital. These should be returned to the hospital or pharmacy. SCIg vials must not be discarded in your household bin.
Q 9: What SCIg products are available in Australia and New Zealand?
The following brands of SCIg are available in Australia and New Zealand:
- Hizentra® AU - CSL Behring
- Hizentra® NZ - CSL Behring
- Hizentra® - CSL Behring
- Cuvitru® - Takeda
- Xembify® - Grifols
The following information has been adapted from the Lifeblood website:
www.lifeblood.com.au/health-professionals/products/fractionated-plasma-products/immunoglobulins/SCIg
SCIg Product - Hizentra® AU and Hizentra® NZ
Hizentra® AU and Hizentra® NZ are SCIg products supplied by CSL Behring and available as a 20% solution (20 g/100 mL) in vial sizes: 1 g/5 mL and 4 g/20mL.
Hizentra® AU and Hizentra®NZ product information and educational materials
This link takes you to CSL Behring's web information about Hizentra® AU and Hizentra® NZ where you can download the product information (PI) sheet for these products.
The PI details the pharmacology, indications, contraindications, precautions, adverse effects, use in pregnancy and lactation, dosage and administration of Hizentra® AU and Hizentra® NZ.
Lifeblood has sent a letter to all Approved Health Providers regarding the introduction of Hizentra® AU and a copy can be found here.
SCIg Product - Hizentra®
Hizentra® is an imported SCIg product, supplied by CSL Behring and available as a 20% solution in vial sizes: 1 g/5 mL, 2 g/10mL, 4 g/20mL and 10 g/50mL.
Hizentra® product information and educational materials
This link takes you to CSL Behring's web information about Hizentra ® where you can download the product information (PI) sheet for this product.
The PI details the pharmacology, indications, contraindications, precautions, adverse effects, use in pregnancy and lactation, dosage and administration of Hizentra®.
SCIg Product – Cuvitru®
Cuvitru® is an imported SCIg product, supplied by Takeda and available as a 20% solution in vial sizes: 1 g/5 mL, 2 g/10mL, 4 g/20mL and 8 g/40mL.
This link takes you to Takeda's web information about Cuvitru® where you can download the product information (PI) sheet for this product.
The PI details the pharmacology, indications, contraindications, precautions, adverse effects, use in pregnancy and lactation, dosage and administration of Cuvitru®.
SCIg Product - Xembify®
Xembify® is an imported SCIg product, supplied by Grifols and available as a 20% solution (20 g/100 mL) in vial sizes: 1 g/5 mL, 2 g/10 mL, 4 g/20mL and 10 g/50 mL.
This link takes you to Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA) website where you can download the product information (PI) sheet for Xembify®.
The PI details the pharmacology, indications, contraindications, precautions, adverse effects, use in pregnancy and lactation, dosage, and administration of Xembify®.
To assist with developing hospital (or treating facility) administration protocols for Xembify®, Consumer Medicine Information is also available on the TGA website.
Lifeblood has sent a letter to all Approved Health Providers regarding the introduction of Xembify® and a copy can be found here.
Q 10: What needs to be checked on SCIg vials before an infusion?
All SCIg vials should be checked for the following prior to an infusion:
- Expiry date on the vial - DO Not Use if out of date.
- Protective cap is in place - DO Not Use if seal is broken.
- Solution in vial is clear - DO NOT USE if solution is cloudy, discoloured or contains particles.
Contact your nurse specialist if any of the above happens.
Q 11: How should SCIg be used when unwell, pregnant or breastfeeding?
Contact your doctor or nurse specialist for further advice if you:
- Are unwell with a fever.
- Suspect you are pregnant.
- Are breast feeding.
Your doctor and nurse specialist will work with you to develop a plan to respond to any adverse reaction.
Q 12: How does SCIg affect vaccinations?
Some immunisations may not be required while on SCIg. Discuss this with your doctor.
Q 13: What documents are required when travelling with SCIg?
 People travelling with SCIg should:
People travelling with SCIg should:
- Plan well in advance before travelling.
- Obtain advice from their doctor or nurse specialist before travelling, especially overseas, as an export permit may be required.
- Use the ASCIA SCIg Travel Plan, completed by their nurse or medical Travel Plans are available on the ASCIA website www.allergy.org.au/hp/papers/ascia-travel-plan-for-scig-patients
- Take their SCIg Travel Plan and Treatment Plan in hand luggage.
- Consider having a dose of Intravenous Immunoglobulin G (IVIg) before travel, which may be a convenient alternative.
- Consider having extra SCIg infusions before and after the trip, for shorter periods of travel.
- Pack SCIg in hand luggage when flying, whilst maintaining the cold chain and remembering to collect it before they leave the plane. SCIg must not be put into checked-in luggage.
- Carry pain medication and a non-drowsy antihistamine in case of adverse reactions.
- Take enough consumable equipment for the time they are away from home.
- Pack enough SCIg for the trip and store this in original packaging until needed, in a cool box or cooler bag. It is important to keep SCIg at an appropriate temperature as specified for the product, at all times. Patients should check product information, and if uncertain, check with their nurse specialist. SCIg should never be stored below 2°C or above 25°C.
Q 14: How can side effects of SCIg be managed?
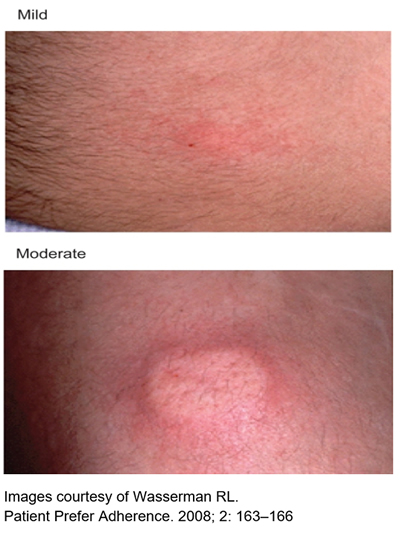 Common local reactions at the infusion site include:
Common local reactions at the infusion site include:
- Mild or moderate swelling (egg sized lump).
- Hardness
- Blanching (whiteness).
- Redness at the infusion site.
These reactions are normal and short lived,usually gone by the next day. They are more common in people who have just started SCIg, especially in the first few months.
Most people start to notice a decrease in local reactions after about 8-10 weeks.
Over time, the skin will “get used” to the repeated infusions, and local reactions will lessen.
Q 15: Should the same SCIg infusion site be used instead of rotating sites?
Using the same site for SCIg infusions can help to reduce the amount of local swelling and redness that can occur after an infusion. However, rotating the infusion site is preferable for some patients, and may reduce the risk of scar tissue developing.
Q 16: What general steps should be taken if an infusion site reaction occurs?
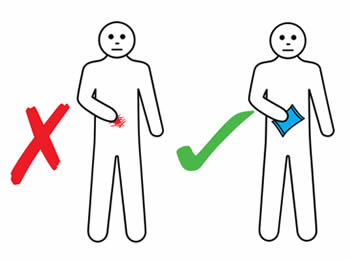 If an infusion site reaction occurs, you should:
If an infusion site reaction occurs, you should:
- Apply gentle massage and warm or cold pack (according to your personal preference) to reduce discomfort. An ice pack should not be applied for four hours post infusion to ensure adequate absorption.
- Not rub or scratch the infusion site.
- Record site reactions in an infusion diary.
- Report unusual site reactions, such as extreme pain or discomfort, blistering or spreading redness to your nurse specialist.
- Refer to the information on the following pages for different ways to manage reactions or problems at the infusion site.
© ASCIA 2025
Content updated May 2025
For more information go to www.allergy.org.au/patients/immunodeficiencies
To support allergy and immunology research go to www.allergyimmunology.org.au/donate
Management guide for SCIg infusion site reactions and problems
|
Site Issue |
Possible Cause/s |
Management Options |
|
Redness |
Common reaction, which usually settles over 24 hours. If redness is excessive:
|
|
|
Swelling |
Common reaction, which usually settles over 24 hours. Swelling usually results from the amount of fluid being infused underneath the skin (amount of swelling should relate to the volume being infused). |
|
|
Itching or burning |
|
|
|
Pain with infusions |
|
|
|
Blanching (whiteness) |
Normal tightening of tissue that can occur as SCIg infuses into the fatty tissue under the skin. |
|
|
Leaking from the infusion site |
|
|
Management guide for other reactions to SCIg